Cruise ships face unique internet challenges due to their reliance on satellite connections with limited capacity. Passengers expect fast, reliable Wi-Fi for streaming, video calls, and uploads, while ships also need bandwidth for critical operations and crew communications. Traditional fixed bandwidth systems fail to handle fluctuating demand, leading to slow speeds and service interruptions.
Dynamic bandwidth allocation solves this by using AI to monitor network traffic and adjust capacity in real-time. This ensures smoother internet for guests, reliable tools for crew, and uninterrupted ship operations – all without increasing bandwidth costs. Cruise lines like Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings have implemented these systems to balance upstream and downstream traffic, prioritize essential services, and share bandwidth across their fleets.
Key takeaways:
- Real-time adjustments improve internet performance during demand spikes.
- Fleet-wide bandwidth sharing prevents resource waste.
- Priority-based allocation ensures critical systems always function.
- Hybrid networks combine satellites, cellular, and in-port Wi-Fi for better connectivity.
Dynamic solutions not only enhance passenger satisfaction but also support essential ship functions and crew welfare.
Connectivity Challenges on Cruise Ships
Managing Thousands of Simultaneous Users
Cruise ships carry thousands of passengers and crew, all expecting reliable Wi-Fi to stay connected. Whether it’s streaming videos, uploading vacation photos, video chatting with loved ones, or scrolling through social media, everyone is vying for bandwidth on a satellite connection with limited capacity. Unlike land-based networks, which can expand infrastructure like fiber or cell towers to meet demand, ships are stuck with the satellite bandwidth they’ve purchased – and that doesn’t come cheap.
The challenge gets even tougher because usage patterns are far from predictable. For instance, after a port visit, hundreds of passengers might upload photos and videos to platforms like Instagram or cloud storage all at once, causing upstream traffic spikes that can overwhelm the network in minutes. On sea days, streaming services dominate bandwidth usage. Special events, such as live sports broadcasts or ship-wide announcements, can also create sudden surges in demand. Without smart management, these peaks can quickly max out the available bandwidth, leading to buffering, failed uploads, and dropped video calls. The fixed capacity of satellite connections simply can’t keep up with these fluctuating demands.
Problems with Fixed Bandwidth Policies
Traditional cruise ship networks often rely on static bandwidth splits to divide capacity between upstream and downstream traffic. For example, a network might allocate 20% of its capacity for uploads and 80% for downloads. While this setup works under normal circumstances, it falls apart when usage shifts unexpectedly. After an excursion, when passengers flood the network with uploads, the upstream allocation gets clogged while the downstream side sits underused, wasting precious satellite resources. By the time IT teams notice and adjust the settings, the demand has often already shifted again, leaving the network struggling to keep up.
Competing Priorities: Operations, Passengers, and Crew
Bandwidth on a cruise ship isn’t just about keeping guests connected. Ship operations rely on a steady connection for navigation systems, engine monitoring, security protocols, regulatory reporting, and financial transactions. Telehealth services, which often involve video consultations, need stable, uninterrupted bandwidth with low latency; any hiccup could force costly medical diversions.
Meanwhile, crew members depend on the network to stay in touch with their families, manage personal finances, and access company systems. These services are no longer seen as optional perks but as crucial for crew retention and welfare.
When all these demands compete for the same limited satellite connection, it creates a dilemma. Spikes in passenger streaming can delay critical telemetry data or disrupt Telehealth consultations. Cruise operators are left with tough decisions: limit crew access, compromise the guest experience, or adopt smarter bandwidth management systems that prioritize essential services without sacrificing entertainment.
Managing Multiple Network Types
Cruise IT teams juggle a mix of GEO, MEO, and LEO satellite links, alongside 4G/5G cellular connections near shore and in-port Wi-Fi or fiber. Each type of connection has its strengths and weaknesses – GEO satellites provide broad coverage but come with higher latency, LEO satellites offer faster speeds and lower latency, and cellular or in-port connections deliver the fastest performance but are only available close to land.
Managing these diverse network types is no easy task. IT teams must decide how to route traffic, blend connections, and account for varying costs and performance levels – all while dealing with constantly changing signal quality as ships move. If each ship operates independently with fixed capacity, one vessel might face severe congestion while another has unused bandwidth that can’t be shared. This inefficient setup not only wastes resources but also creates inconsistent experiences for guests across the fleet. The complexity of managing these networks highlights the need for a system that can dynamically adjust bandwidth based on real-time conditions.
Why Traditional Bandwidth Management Falls Short
Fixed Capacity Splits Create Waste
Traditional bandwidth management struggles to keep up with shifting demands. Unlike dynamic systems that adapt in real time, static capacity splits often leave satellite resources underutilized. For example, when demand shifts from general browsing to upload-heavy tasks like cloud syncing or video calls, fixed splits can’t adjust to meet the need. Cruise lines face a tough choice: pay for excessive bandwidth that might not always be used or risk poor service by under-provisioning. Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings discovered that fixed splits fell short for uplink-heavy needs, such as video conferencing. As one industry analysis pointed out, older connectivity solutions "lack the intelligence and adaptability to optimize bandwidth where and when it matters most."
Manual Adjustments Are Too Slow
When demand spikes suddenly – whether from video calls, streaming, or cloud syncing – manual bandwidth reconfiguration just can’t keep up. This reactive approach not only delays performance improvements but also adds extra work for IT teams. Cruise lines are left with two bad options: endure poor service during high-demand periods or pay for costly satellite bandwidth contracts to avoid potential bottlenecks. This outdated method limits the overall efficiency of the fleet and highlights the need for more flexible, responsive solutions.
Isolated Ship Networks Waste Resources
Another inefficiency arises from the isolated management of bandwidth on individual ships. Fixed allocations mean that if one ship is underutilizing its bandwidth while another faces high demand, resources go to waste. To avoid service disruptions, cruise lines often allocate bandwidth based on worst-case scenarios, leading to significant over-provisioning across the fleet. Cameron Lee, Senior Director of Onboard Revenue at Norwegian Cruise Line, noted that adopting dynamic technology allowed them to "manage our total bandwidth as one", delivering a better experience for passengers without increasing bandwidth contracts.
LAN Ho! Navigating Cruise Ship Networking
How Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation Works
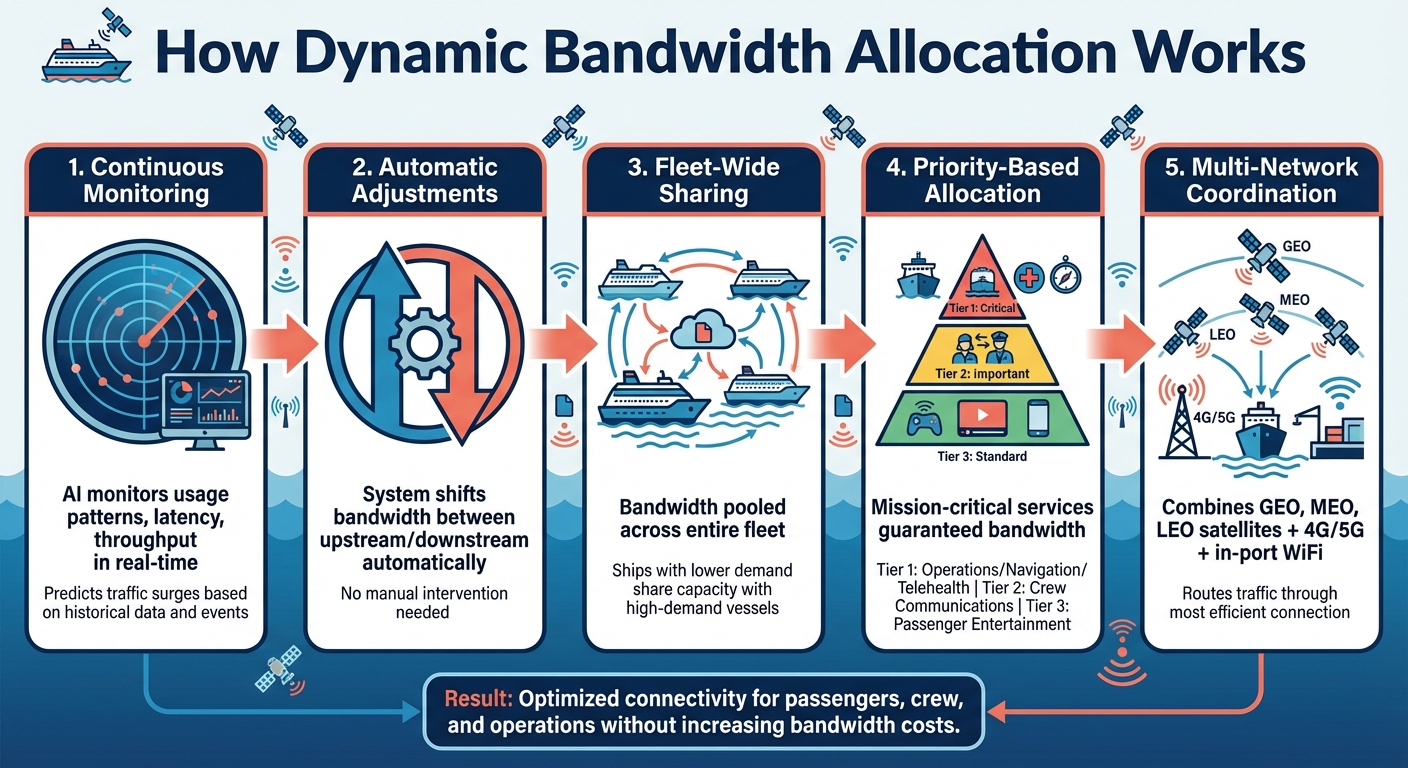
How Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation Works on Cruise Ships
Continuous Monitoring and Traffic Prediction
Dynamic bandwidth allocation relies on real-time AI analytics to keep a close eye on usage patterns, latency, throughput, and application quality. By examining historical data, time of day, and scheduled events, the system can predict traffic surges. For example, it might anticipate a spike in upstream demand when passengers upload photos and videos after returning from port. This proactive approach ensures that congestion is avoided and critical applications, like Telehealth or crew communications, remain reliable.
With these insights, the system swiftly adjusts and redistributes bandwidth to match changing demands.
Automatic Upstream and Downstream Adjustments
Gone are the days of rigid bandwidth splits. Dynamic systems automatically shift resources based on real-time needs. If passengers are streaming videos or engaging in upload-heavy activities, the system reallocates bandwidth accordingly. Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings has adopted this technology across its fleet, allowing bandwidth ratios to adapt continuously. This improvement enhances connectivity for both guests and crew without requiring expanded bandwidth contracts.
Shared Bandwidth Pools Across the Fleet
Instead of assigning a fixed capacity to each ship, dynamic allocation enables seamless sharing of resources among vessels. Ships with higher demand receive additional capacity, while those with lower usage contribute their spare bandwidth to the collective pool. This approach minimizes waste and ensures a consistent experience for all users. By orchestrating bandwidth across the fleet, operators can efficiently manage total capacity without increasing contract limits.
Priority-Based Allocation by Application and User Type
Once bandwidth is pooled and distributed across the fleet, the system prioritizes allocation based on the importance of applications and user groups. Not all traffic is treated equally. Mission-critical services, such as operational systems, navigation data, and Telehealth, are guaranteed bandwidth. Crew communications, which require stable two-way connectivity, are prioritized over less essential passenger activities like social media browsing. This tiered system ensures that vital services perform optimally, even during peak usage, while maintaining a balanced experience for all users.
Coordinating Multiple Network Types
Modern cruise ships depend on a mix of connectivity sources, including GEO, MEO, and LEO satellites, as well as 4G/5G cellular networks and in-port Wi-Fi. Dynamic bandwidth allocation combines these diverse connections into a unified network, adapting to real-time conditions. It analyzes the performance of each connection and routes traffic through the most efficient option. For instance, low-latency LEO satellites handle real-time communications, GEO satellites manage bulk data transfers, and in-port Wi-Fi is utilized when docked. This integration ensures smooth coverage and efficient bandwidth use.
Together, these dynamic mechanisms work to deliver optimized connectivity, meeting the unique challenges of maritime environments.
sbb-itb-bda822c
Implementing Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation
Automatic Capacity Adjustments for Better Performance
Cruise operators use systems that automatically adjust bandwidth between upstream and downstream traffic based on real-time needs. For example, Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings has adopted this method to improve services like cloud synchronization and video calls without requiring extra bandwidth or manual adjustments. When passengers return from port visits and upload photos, the system reallocates unused downstream capacity to upstream traffic. Later, during peak evening hours when streaming spikes, it shifts capacity back to downstream usage. Onboard quality-of-service policies ensure latency-sensitive applications, like video calls, are prioritized, while bulk transfers are throttled during busy times. These dynamic adjustments, combined with fleet-wide resource sharing, further boost efficiency.
Sharing Bandwidth Across the Fleet
Fleet-wide bandwidth sharing treats satellite capacity as a centralized resource rather than assigning fixed allocations to each ship. For instance, when a ship docks and connects to terrestrial backhaul, its unused satellite bandwidth is redistributed to vessels at sea facing higher demand. Marlink’s system for MSC Cruises provides several hundred Mbps of shared capacity, dynamically allocated to meet varying seasonal and operational needs. A centralized orchestration system oversees usage, enforces policies, and ensures compliance with contractual limits.
Guaranteed Bandwidth for Critical Systems
To maintain reliability for essential services, operators reserve specific bandwidth for critical applications, using strict quality-of-service policies and guaranteed minimum rates for each vessel. When network congestion occurs, nonessential guest traffic is throttled first, ensuring uninterrupted access for priority services. Platforms also allow for instant bandwidth boosts via APIs, which is crucial for emergency Telehealth or remote maintenance needs. NT Maritime demonstrates this approach by integrating dedicated VLANs and prioritizing clinical endpoints, ensuring dependable connectivity for Telehealth and other mission-critical operations. These reserved capacities work seamlessly alongside hybrid network setups.
Combining Multiple Network Paths
A hybrid WAN approach blends various connection types to adapt dynamically to changing conditions. Satellite connectivity serves as the baseline, while terrestrial cellular networks and in-port Wi-Fi handle high-volume traffic at lower costs when available. Policy-based routing ensures critical real-time services use the most reliable connections, while bulk tasks like updates are directed to more cost-effective networks. Platforms also include automatic failover and load balancing, allowing traffic to shift seamlessly if a connection degrades. This creates a self-healing network. NT Maritime, for instance, integrates Starlink satellite service – offering download speeds up to 220 Mbps, upload speeds up to 40 Mbps, and latency under 99 ms – alongside onboard Wi-Fi and secure communication networks. This combination ensures consistent, cost-effective connectivity for passengers and critical operations alike.
How IT Platforms Support Dynamic Bandwidth Management
Unified Network and Communication Management
Maritime IT platforms bring together various connectivity sources – like satellite (LEO, MEO, GEO), 5G/LTE, in-port fiber, and onboard Wi-Fi – into one centralized system. This integration allows cruise operators to manage passenger internet, crew communication, and operational systems from a single dashboard. IT teams can prioritize bandwidth to ensure navigation systems and safety applications always have the capacity they need, while guest streaming and crew services use the remaining bandwidth. By consolidating control, operators can quickly reallocate resources to meet changing demands across the fleet. Real-time analytics provide insights into usage by application, user group, and ship location, helping operators identify congestion points and adjust policies without manually reconfiguring each vessel. This streamlined approach ensures critical services receive the bandwidth they require.
For example, NT Maritime’s platform combines communication tools – such as messaging, video calling, voicemail, and onboard calling – with secure operational networks and high-speed internet. It applies role-based policies to automatically prioritize essential services during peak usage, ensuring smooth communication for both guests and crew.
Reliable Bandwidth for Telehealth and Critical Services
Telehealth services, like remote consultations and diagnostics, rely on stable, low-latency connections. Any disruptions, such as jitter or packet loss, can interfere with medical assessments or delay urgent decisions. Dynamic IT platforms address this by instantly prioritizing bandwidth when telemedicine sessions begin. During periods of congestion, non-essential traffic is throttled to protect telehealth connectivity. This targeted management also ensures reliable communication for everyday needs, benefiting both passengers and crew.
NT Maritime’s platform integrates telehealth technologies with dedicated network paths to maintain consistent connectivity for remote medical consultations, even when thousands of passengers are streaming or uploading content. With speeds of up to 220 Mbps for downloads, 40 Mbps for uploads, and latency under 99 milliseconds, the system supports both routine telehealth appointments and emergency diagnostics without interruptions.
Stable Communication Tools for Passengers and Crew
Ensuring stable messaging, video calls, and voicemail during high-demand times requires smart quality-of-service policies. These policies recognize real-time communication protocols and assign them higher priority over less urgent data transfers. Modern platforms route time-sensitive communications through the most efficient network paths, maintaining reliable service quality.
NT Maritime’s communication solutions, which include integrated messaging, video calling, and voicemail over ship Wi-Fi, benefit from this dynamic routing. Whether using fiber in port or satellites offshore, the platform ensures dependable service that boosts guest satisfaction and crew morale. Centralized fleet-wide management also allows IT teams to monitor call quality, session stability, and service performance, enabling them to fine-tune policies based on real-time data.
Conclusion
Dynamic bandwidth allocation is revolutionizing how cruise ships manage connectivity, shifting from rigid, fixed policies to a smarter, demand-driven system. This approach continuously adjusts resources in real-time, ensuring smooth performance for both leisure and critical operations. Whether guests are uploading vacation photos or streaming their favorite shows during peak hours, this system ensures reliable Wi-Fi while operators maintain essential services and maximize the value of their satellite contracts.
But it’s not just about improving user experiences. Dynamic allocation also brings operational and financial advantages. By treating bandwidth as a shared, flexible resource across an entire fleet, it eliminates the inefficiencies of fixed policies. Automation powered by AI further reduces the need for manual IT intervention. A great example of this is Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings, which successfully implemented dynamic bandwidth management technology in 2023.
Modern solutions take it a step further by combining multiple connection types – satellites, cellular networks, and in-port fiber – to enhance both availability and reliability. These systems automatically pick the best connection path, balancing cost and performance. This ensures dependable connectivity for mission-critical tasks while maintaining a consistent experience for passengers and crew, no matter where the ship is.
NT Maritime is at the forefront of these advancements, offering sophisticated IT and communication solutions that bring dynamic bandwidth policies to life. Their platform integrates features like calling, messaging, video conferencing, and telehealth services, alongside secure networks and high-speed internet. With download speeds of up to 220 Mbps, upload speeds of 40 Mbps, and latency under 99 milliseconds, NT Maritime ensures seamless connectivity for both everyday needs and critical operations.
As passengers increasingly expect "onshore-quality" internet and ships introduce more digital services, traditional bandwidth management simply can’t keep up. NT Maritime’s cutting-edge solutions help cruise operators adopt dynamic bandwidth capabilities more quickly, reduce risks, and stay ahead of future demands. This smarter approach to connectivity not only supports new digital services but also improves crew well-being and enhances safety through data-driven operations.
FAQs
How does dynamic bandwidth allocation enhance internet connectivity on cruise ships?
Dynamic bandwidth allocation improves internet connectivity on cruise ships by smartly managing bandwidth in real time. This allows passengers and crew to enjoy smoother browsing, dependable video calls, and steady access to online services – even during busy periods.
By adjusting to fluctuating demand, this system reduces network congestion and ensures the available resources are used efficiently, creating a more reliable online experience for everyone on the ship.
How does AI improve connectivity on cruise ships?
AI plays a key role in improving connectivity on cruise ships by managing bandwidth allocation and forecasting network demand. It adjusts resources in real-time to keep communication running smoothly, even when usage is at its highest.
This smart system ensures consistent access to high-speed internet, onboard communication platforms, and other critical services, making life at sea more convenient and enjoyable for both passengers and crew.
How do cruise ships ensure reliable internet for passengers while maintaining critical operations?
Cruise ships rely on dynamic bandwidth allocation to handle internet usage efficiently. This system ensures critical operations – like safety protocols, navigation, and crew communications – get top priority. The leftover bandwidth is then made available for passengers.
This approach allows cruise lines to maintain essential functions while still offering passengers a dependable and enjoyable internet connection throughout their trip.