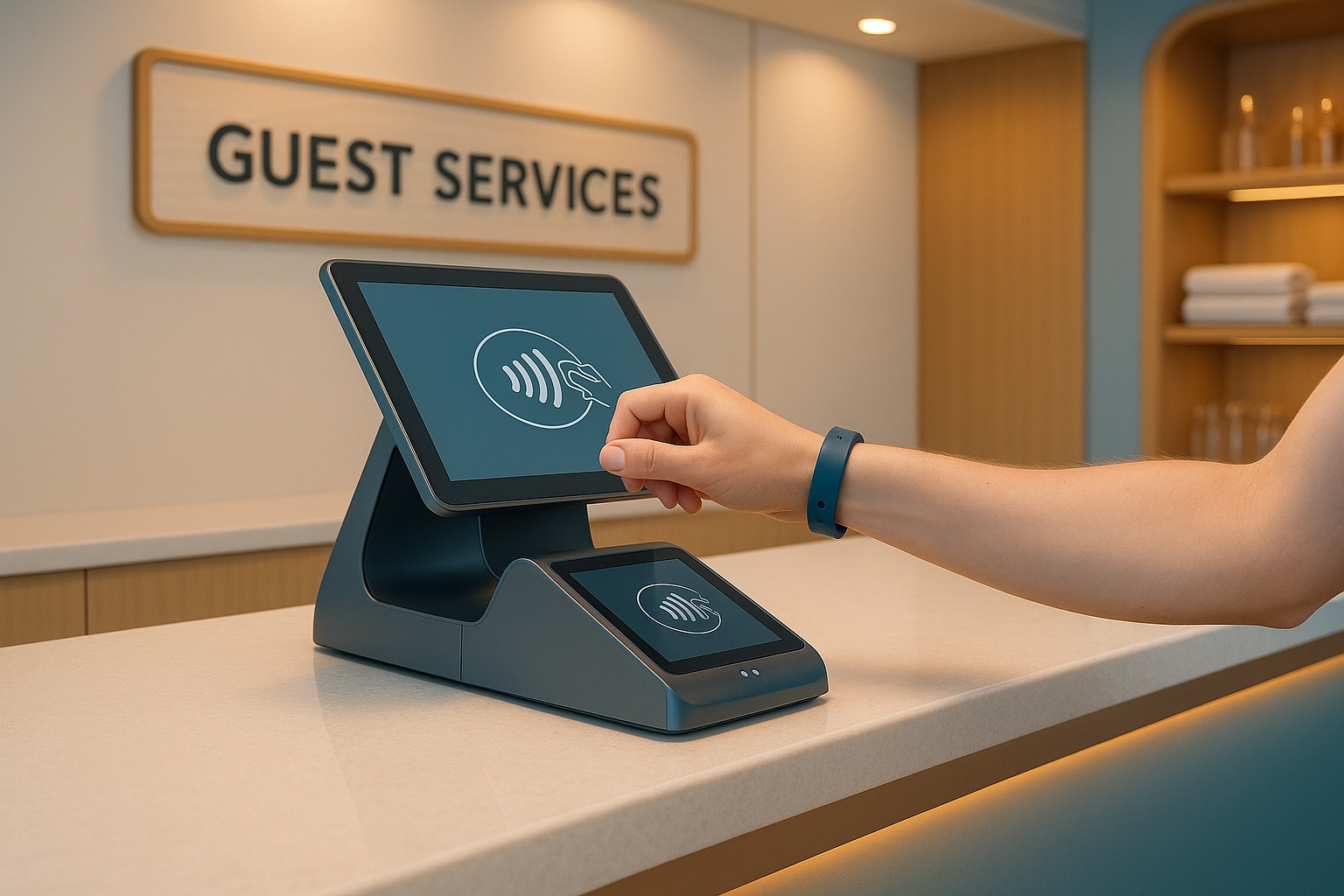
POS systems on cruise ships simplify transactions, link guest purchases to cabin accounts, and improve service across bars, restaurants, shops, spas, and excursions. These systems enable cashless payments via boarding cards or wearables, consolidating charges into a single bill. Integration with property management systems ensures accurate billing and personalized services, while offline functionality addresses connectivity challenges at sea. Features like mobile POS devices, self-service kiosks, and real-time inventory tracking enhance crew efficiency and guest satisfaction by reducing wait times, minimizing errors, and offering tailored experiences. Reliable onboard networks are critical to keeping these systems operational, with providers like NT Maritime supporting secure and high-speed communication. Future advancements may include AI-driven analytics and biometric payments, though challenges like data security and cost remain.
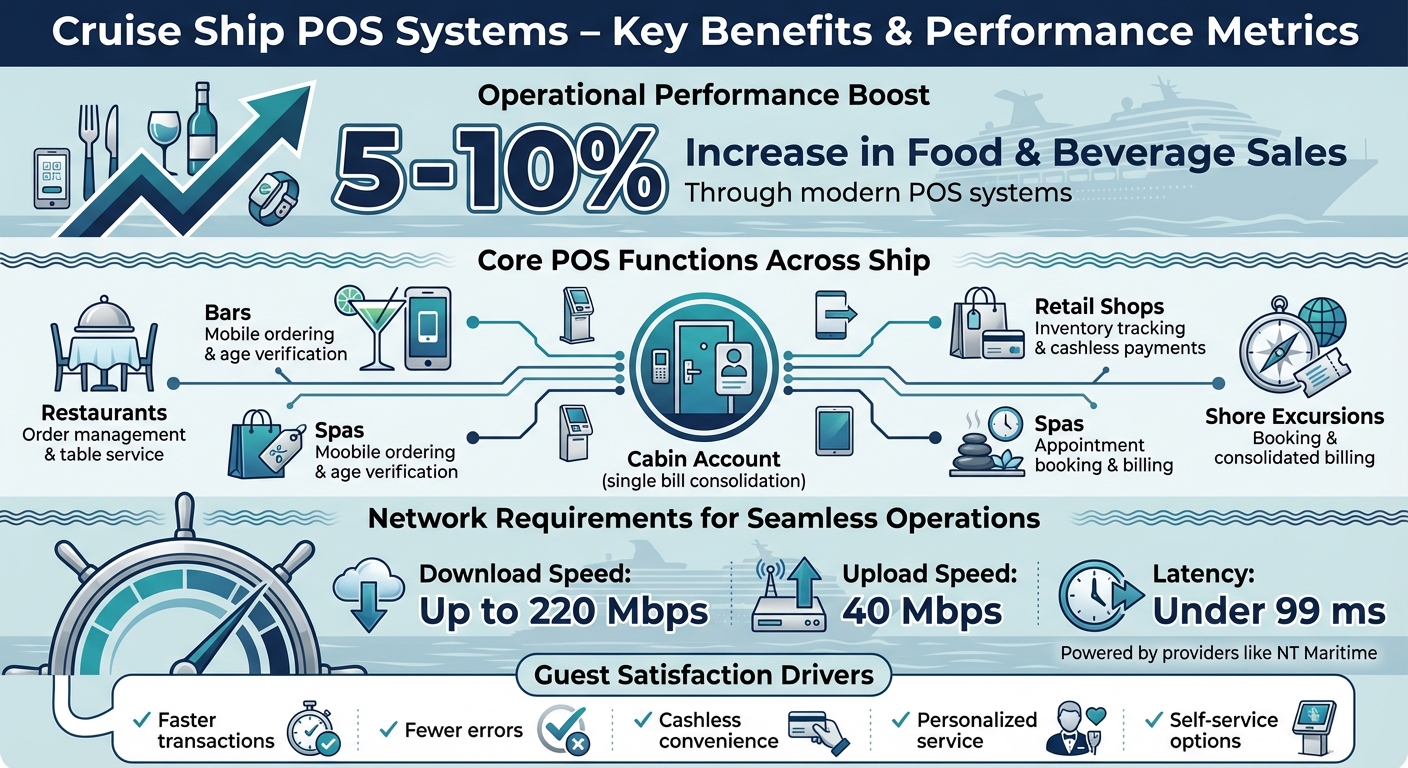
Key Benefits and Performance Metrics of Cruise Ship POS Systems
Navigate the C: A Deep Dive into CruisePAL POS and Maritime Technology
How POS Systems Improve Cruise Operations
Modern POS systems handle a wide range of tasks, from managing orders and payments to tracking inventory and generating reports. These systems are vital across various onboard services, including restaurants, bars, retail shops, spas, and even shore excursions. Let’s dive into how these tools streamline operations, speed up transactions, and improve crew efficiency.
Faster Transactions and Fewer Errors
With mobile POS devices, crew members can take orders directly from guests – whether at a table or poolside – eliminating the need to visit a fixed terminal. Orders are sent instantly to kitchens or bars, which not only speeds up service but also minimizes mistakes. According to IBS Software, cruise lines using modern POS systems can boost food and beverage sales by 5–10% thanks to smoother processes and better upselling opportunities. Additionally, integrating dining POS systems with galley management software provides real-time updates, further reducing errors. Cashless billing simplifies transactions by automatically posting charges to a guest’s account, removing the hassle of currency exchange and even automating age verification for restricted items [7].
Better Crew Workflows
POS systems don’t just enhance guest interactions – they also improve how the crew operates. Mobile and tablet-based POS devices allow staff to check table availability, estimate wait times, and take orders without stepping away from guests. This streamlined approach is especially valuable during busy dining hours or embarkation. For example, tablet eCheckIn modules used at terminals and hotel lobbies enable staff to process guests more quickly, even offline, cutting down embarkation times and balancing workloads. Integration across POS modules ensures crew members can easily shift between service areas, reducing both training time and the likelihood of errors.
Inventory Tracking and Revenue Management
POS systems also shine when it comes to inventory and revenue management. Historical data from these systems helps cruise lines predict demand and analyze purchasing trends. Galleys, for instance, can use this data to estimate daily or cruise-specific food preparation needs, reducing waste while meeting demand. Real-time inventory tracking ensures that bars, shops, and spas maintain optimal stock levels, while sales data synced with headquarters enables centralized reporting. These insights allow cruise operators to make smarter decisions about purchasing, staffing, and menu updates, all of which contribute to a better guest experience [7].
How POS Systems Affect Guest Satisfaction
While improving operations is essential, the true success of a POS system lies in how it enhances the guest experience. Modern POS technology plays a key role in boosting guest satisfaction by speeding up transactions, minimizing errors, and offering more personalized service. When guests spend less time waiting and more time enjoying their cruise, they’re more likely to return. These advancements go beyond efficiency – they create a smoother, more enjoyable cruise experience through faster service and tailored interactions.
Service Quality and Convenience
Fast service is a cornerstone of guest satisfaction. Mobile POS devices allow crew members to take orders right at the table or even poolside, instantly relaying them to kitchens or bars. This ensures that food and drinks arrive quickly and with fewer mistakes. By cutting down on wait times and reducing order errors, modern POS systems make dining experiences smoother, encouraging repeat purchases. According to Agilysys, mobile POS significantly enhances service speed and boosts overall venue ratings, which directly impacts guest satisfaction.
When staff can stay with guests instead of constantly returning to fixed terminals, the interaction feels more personal and attentive. This not only improves guest experiences but also leads to better online reviews and higher tips. For U.S. guests used to the convenience of tap-and-go payments, cashless systems linked to stateroom cards or wearables eliminate the hassle of carrying wallets or dealing with currency exchanges [7].
Personalization and Loyalty Programs
Modern cruise POS systems collect detailed guest preferences – like favorite drinks, dining habits, allergies, and past purchases – that crew members can access instantly. This information allows for highly personalized service. For instance, a bartender might welcome a returning guest by suggesting their go-to cocktail, or a server could recommend gluten-free dishes when an allergy is flagged. Built-in "smart prompts" provide staff with tailored suggestions, making service feel thoughtful and seamless.
Loyalty program integration takes personalization even further. Guests can earn and redeem points, use onboard credits, and enjoy tier-specific perks directly at checkout. The POS system simplifies complex entitlements, like beverage package coverage, making the process smooth and hassle-free. This not only enhances the value of loyalty memberships but also provides cruise lines with valuable data to craft targeted offers that encourage repeat bookings.
Self-Service and Multi-Channel Options
Today’s travelers want more control over how and when they access onboard services. Self-service options powered by POS systems – like in-cabin TV ordering, mobile apps, and kiosks – let guests order meals, book excursions, and review bills on their own schedule, without waiting for staff. Some systems even allow meal pre-orders for specific times, helping guests coordinate dining with shows or port schedules.
These options appeal especially to tech-savvy guests and those who prefer minimal interaction. By enabling off-peak orders and spreading demand throughout the day, self-service options reduce congestion during busy periods and give guests more flexibility. Multilingual support on guest-facing screens and apps also helps international passengers navigate services with ease, reducing confusion and order errors [7]. For U.S. guests, clear currency formatting ($25.00), 12-hour time displays, and straightforward billing breakdowns on digital receipts help prevent disputes and build trust.
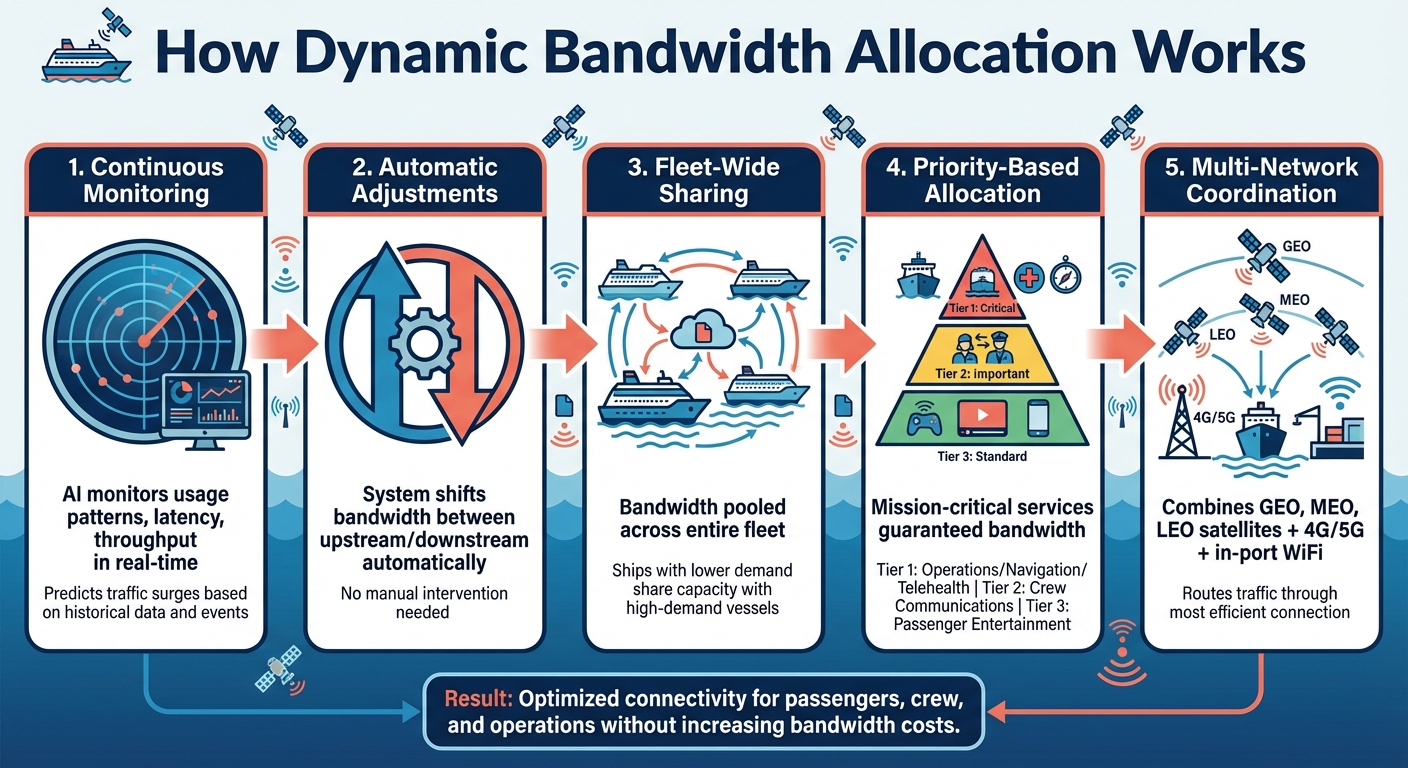
All of these features depend on a reliable onboard network. High-speed, secure connectivity is essential to keep mobile POS systems, guest apps, and in-cabin ordering running smoothly. Providers like NT Maritime ensure that even in challenging maritime conditions, these systems remain fast and dependable, supporting a seamless guest experience.
sbb-itb-bda822c
POS Integration with Cruise IT Systems
For a cruise POS system to function effectively, it must integrate seamlessly with both onboard and shore-based IT systems. When platforms like POS, property management, inventory, and communication systems are interconnected, cruise lines can provide faster service, minimize billing errors, and gain valuable insights into revenue and guest behavior across their fleet. This interconnectedness helps streamline operations and elevates the guest experience across all onboard services.
Connection with Property Management Systems
The integration of POS systems with a ship’s Property Management System (PMS) transforms every guest’s boarding card or wearable device into a universal payment method. Transactions are instantly posted to the cabin folio via the PMS, consolidating all charges into a single, unified bill. This setup enforces credit limits, supports split billing, and applies service charges or discounts automatically based on predefined rules. Guests can access detailed, time-stamped folios through kiosks, in-cabin TVs, or mobile apps. This level of transparency not only builds trust but also simplifies the settlement process at the end of the cruise.
Coordinating Shipboard and Shore Operations
Cruise operations rely heavily on synchronized data between the ship and headquarters. Onboard POS systems send detailed sales data, revenue by outlet, inventory updates, and guest spending patterns to shore-based systems. At the same time, headquarters provides the fleet with updated item catalogs, menus, pricing, promotions, tax rules, and configuration changes to ensure consistency across all ships.
Digital twin models allow for autonomous onboard operations, reconciling data later when connectivity improves. Synchronization typically happens when ships are docked or when satellite connections are strong, with systems prioritizing key data like master records and summarized sales. This coordination supports daily operations and strengthens the overall IT ecosystem. It also gives finance and revenue management teams a consolidated view of daily revenue, onboard spending per guest, and outlet performance. With these insights, shore-side teams can adjust pricing, launch targeted promotions, and optimize inventory based on historical consumption trends.
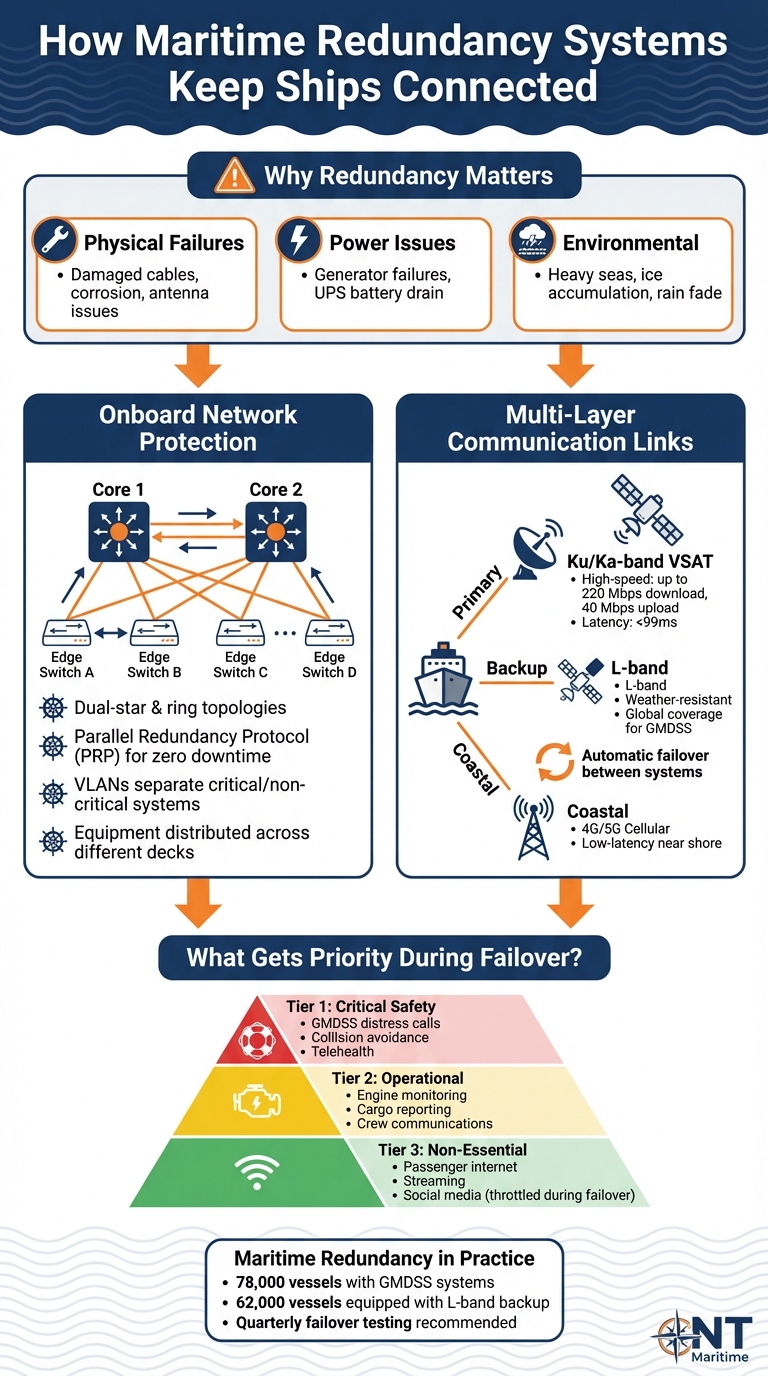
Network Reliability and Communication Infrastructure
All these integrations hinge on the availability of a secure, high-speed onboard network and dependable ship-to-shore communication. For shipboard POS systems, dedicated IP networks support both fixed and mobile POS devices. Quality of Service (QoS) policies ensure transactional data is prioritized over non-essential guest internet usage, while VLAN segmentation and firewalls help meet PCI-DSS security standards.
Providers like NT Maritime play a critical role in delivering the secure, high-availability communication networks that make these integrations possible. Their solutions combine satellite and hybrid links with VPNs, traffic prioritization, and encryption to safeguard data exchanged between onboard and shore systems. NT Maritime offers high-speed internet with download speeds up to 220 Mbps, upload speeds of 40 Mbps, and latency under 99 ms. Their networks can allocate dedicated, QoS-protected bandwidth for POS transactions, reducing the risk of disruptions caused by guest streaming or crew internet use. This ensures smooth transaction processing, timely data synchronization, and real-time access to guest information, no matter where the ship is located.
Future Developments in Cruise POS Systems
New Technologies in POS Systems
The next generation of cruise POS systems is set to embrace AI-powered platforms that can analyze guest behavior in real time. These systems aim to deliver dynamic pricing, tailored promotions, and precise recommendations. Imagine a system so intuitive that it predicts what a guest might want and enables crew members to make personalized suggestions at just the right moment.
Right now, most cruise lines rely on boarding cards as cashless payment tools[7]. However, the future may see a shift toward biometric payment systems, such as facial recognition or fingerprint scanning. This technology could simplify transactions at bars, restaurants, and onboard shops while minimizing the hassle of lost or forgotten cards. Of course, these advancements would need to address privacy concerns and comply with international data protection laws.
Mobile and self-service ordering options are already making waves, allowing guests to order through interactive TVs or mobile apps from the comfort of their cabins. Looking ahead, POS systems could integrate with smart cabin technologies, using sensor data and guest preferences to present timely offers – like discounts on spa treatments, exclusive dining experiences, or shore excursions. For these features to work seamlessly, cruise ships will need robust onboard networks, such as those offered by NT Maritime, to support real-time analytics and mobile POS functionality.
While these innovations are exciting, they also bring challenges that need further exploration.
Research Gaps
Despite the promise of these advancements, there are still unanswered questions about their long-term impact and security. For example, while some cruise lines report sales boosts of 5 to 10 percent, there’s limited research comparing different platforms or analyzing whether these gains are sustainable over time. Factors like ship size, itinerary, and passenger demographics could all influence these outcomes, but data on these variables remains sparse.
Another pressing issue is guest privacy. As POS systems gather detailed insights into purchasing habits, dietary choices, and spending patterns, questions arise about how this data is stored, protected, and used. This becomes even more complex when vessels operate under varying international data protection laws. Additionally, as POS systems integrate with other shipboard technologies like door locks and communication networks, they create more entry points for potential cyberattacks. Unfortunately, best practices for securing these interconnected systems in maritime settings are not yet clearly defined.
Finally, cruise lines would benefit from a thorough cost–benefit analysis of adopting advanced features like AI-driven analytics, biometric payments, and mobile POS systems. Such studies could help operators weigh the potential advantages against the financial and logistical challenges of implementing these technologies across diverse fleets.
Conclusion
Modern POS systems have become the backbone of cruise guest services, touching every revenue-generating area – from dining and bars to retail shops, spas, and shore excursions. Studies indicate that mobile POS platforms not only speed up transactions but also minimize errors and enhance crew efficiency. These improvements translate to a 5–10% boost in food and beverage sales, while also increasing guest satisfaction.
Beyond these operational perks, today’s POS systems connect seamlessly with tools like PMS, inventory management systems, and CRM platforms. This integration provides a comprehensive view of each guest and delivers real-time insights that fine-tune pricing, inventory, and promotions. At the same time, they streamline self-service options and simplify crew workflows.
However, none of this would be possible without reliable, high-speed onboard networks. These networks ensure POS systems can operate smoothly, even offline, and allow timely synchronization of ship-to-shore data. NT Maritime’s secure, high-bandwidth solutions meet these demands, maintaining functionality despite occasional satellite connectivity challenges. This solid infrastructure paves the way for the next wave of POS advancements.
FAQs
How do POS systems improve the guest experience on cruise ships?
Cruise ships rely heavily on POS systems to make transactions smoother and reduce wait times, allowing guests to focus on enjoying their vacation without unnecessary delays. Whether it’s ordering a drink or purchasing a souvenir, these systems ensure everything runs efficiently.
Beyond convenience, POS systems also help deliver a personal touch. By keeping track of guest preferences and purchase histories, they allow staff to offer services that feel customized to each individual. From seamless billing to quick access to onboard amenities, these systems play a big role in creating a hassle-free and unforgettable cruise experience.
What challenges come with using AI and biometric payments in cruise POS systems?
Integrating AI and biometric payment systems into cruise POS systems isn’t without its hurdles. One major concern is data security and privacy. These systems process sensitive personal information, making robust protection measures a must.
Another challenge lies in merging these advanced technologies with existing systems. This can be a tricky and time-intensive process, requiring careful planning and execution.
There’s also the issue of potential technical glitches. While not common, any system failures can disrupt operations and negatively affect the guest experience. Beyond the technical side, gaining passenger trust is crucial. Some may feel uneasy about how their data is being collected, used, or stored, making transparency and communication essential for acceptance.
How do cruise POS systems protect guest data and ensure privacy?
Cruise POS systems prioritize the security of guest data by employing encryption technologies that shield sensitive information during transactions. These measures ensure that data remains protected from potential threats.
To further strengthen security, these systems enforce strict access controls, allowing only authorized staff to handle critical information. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and ensures data integrity.
Moreover, secure communication protocols are used to block any unauthorized attempts to intercept or compromise data. These safeguards not only protect guest information but also contribute to a safer and more enjoyable experience for everyone on board.